The nitty gritty science behind irido
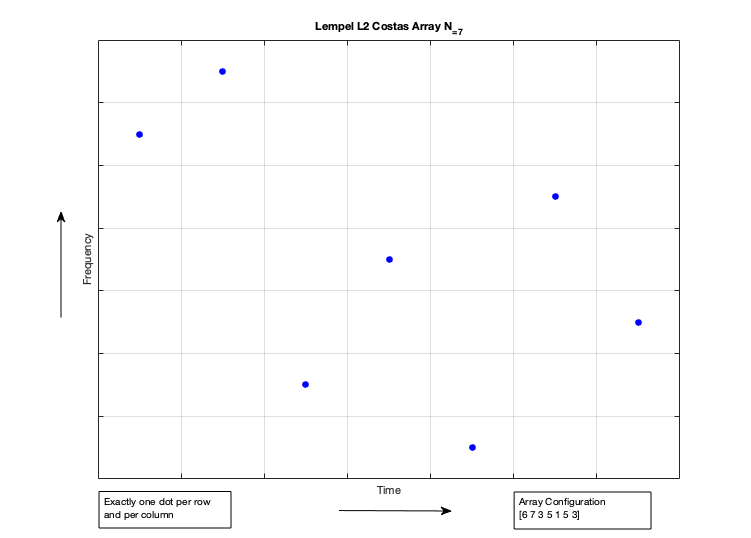
irido is a Sonic Crystal based on a higher order Costas Array (Proposed by J.Costas in the 1960s)
that are widely used in RADOR, SONAR and encryption algorithms.
Keywords : audio/acoustic experience, circular acoustics, modular acoustics, acoustic effect, sonic crystal
What is a Sonic Crystal ?
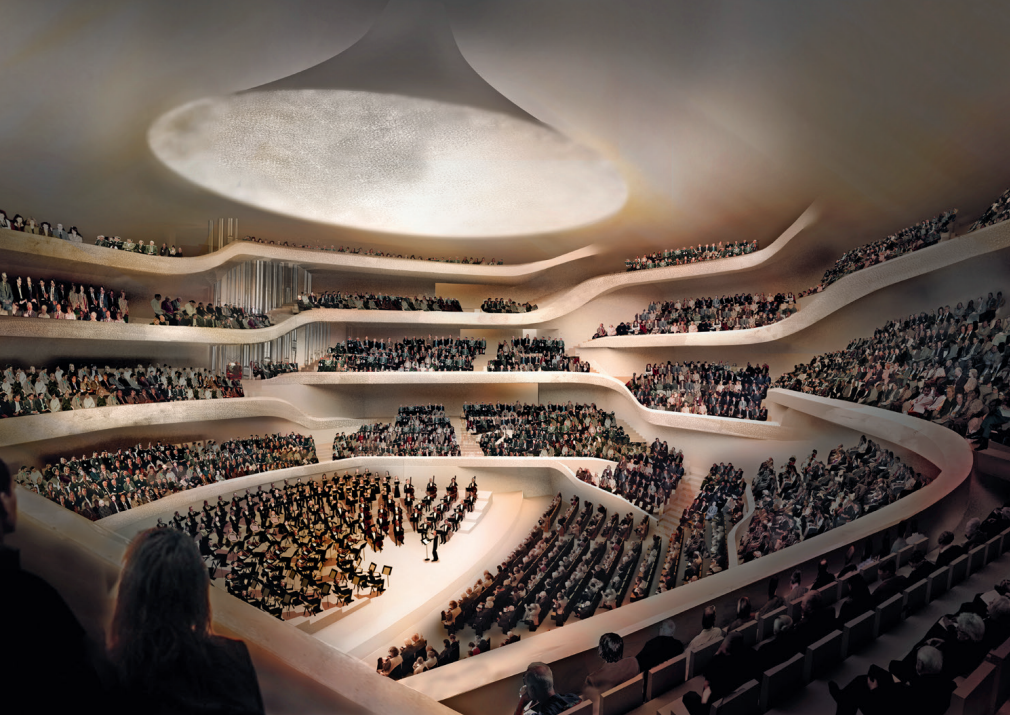

How far can modular acoustics go? irido utlizes Computational Acoustics commonly employed among the most celebrated concert halls in the world, coupled with lab measurements at TU Delft to make informed decisions on acoustic properties, offering a level of portability and modularity that surpasses traditional surface diffuser counterparts (i.e. QRD and skyline) and conventional physical acoustic effects (i.e. echo chamber and corridor).
The name of irido stems from the latin word : iridophore, referring to its capability reflecting sound back at different wavelengths and possibly in different polarities.
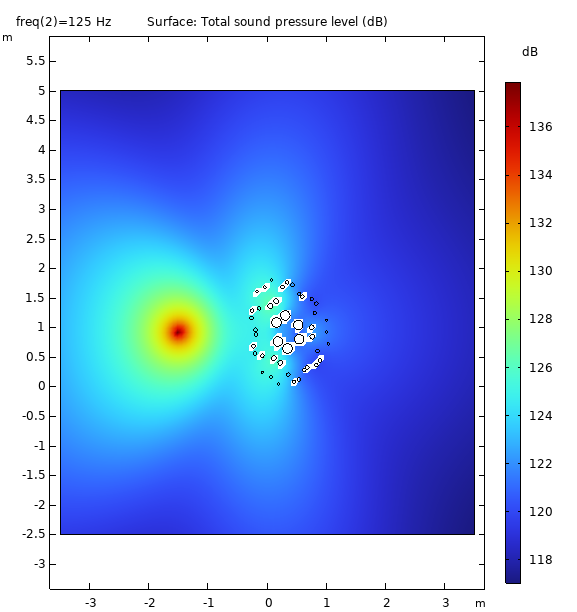
It has application for Insertion Loss in Near Field condition creating a large Geometric Shadow Zone (GSZ) and contributes to Diffuse Field in Far Field condition
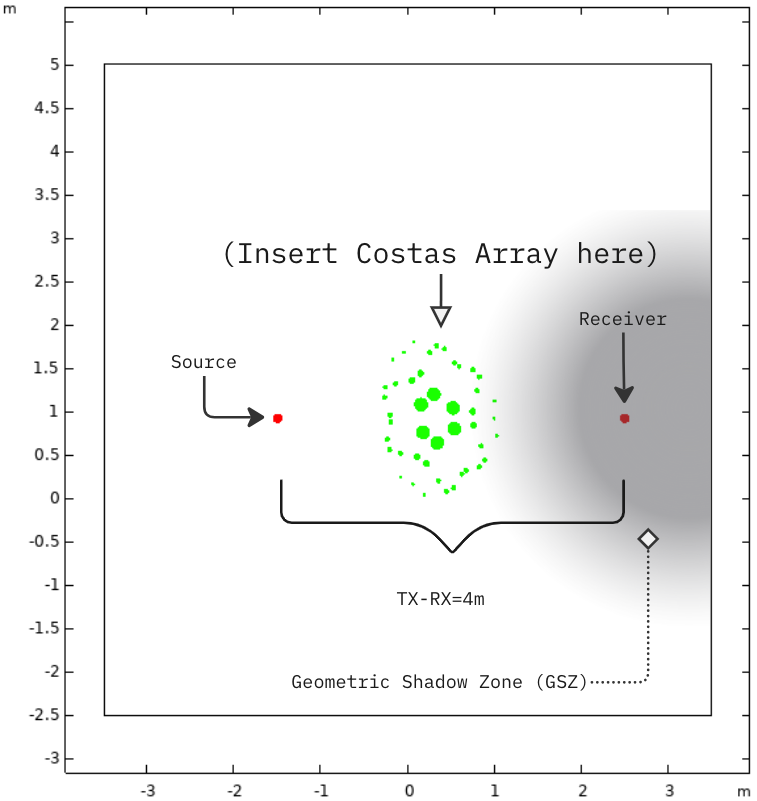
.png)
Data Auralization (3D)
The ability to hear how irido sounds provide further insights that CANNOT be visualized by figures and tables.
Data Visualization (2D)
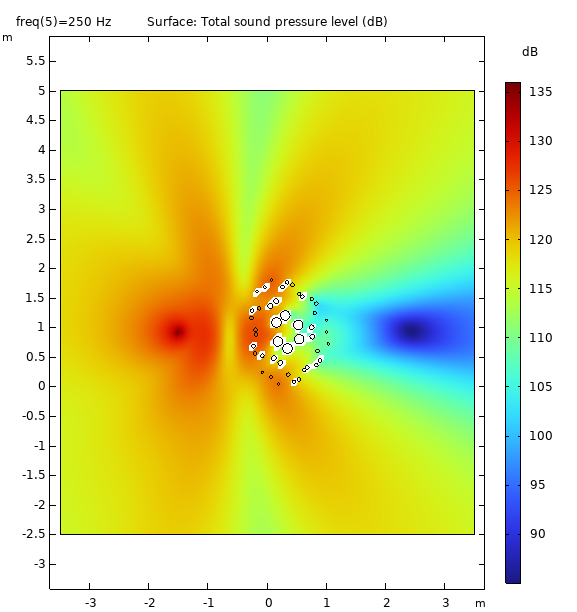
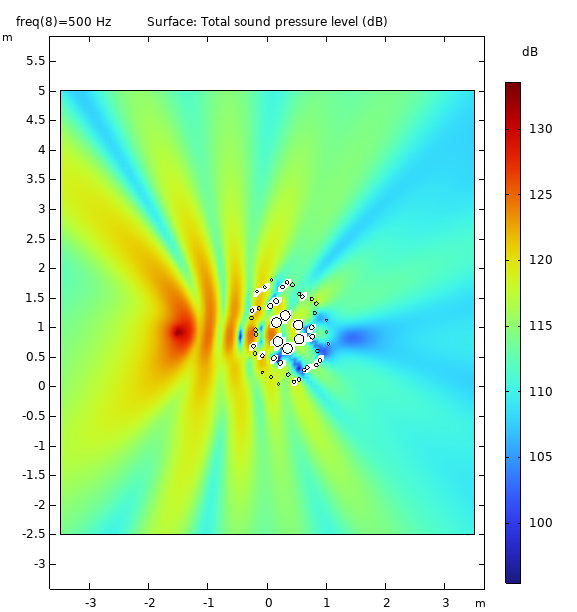
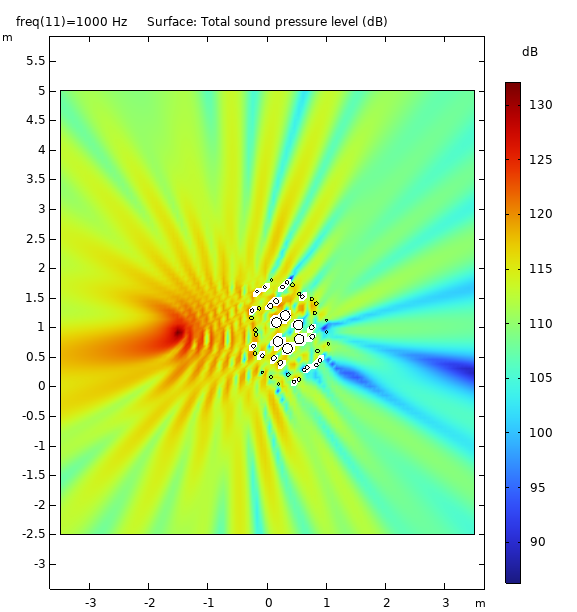
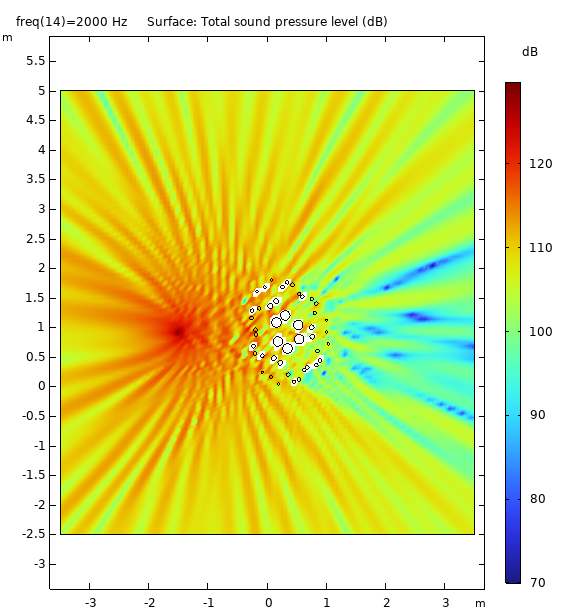
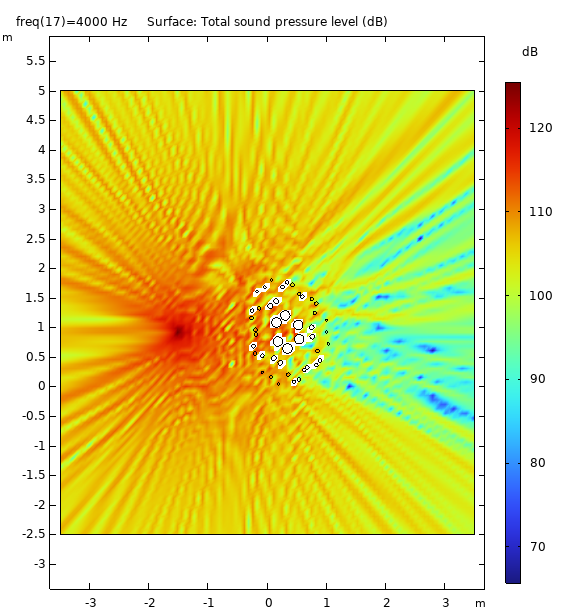
Data Visualization (3D)
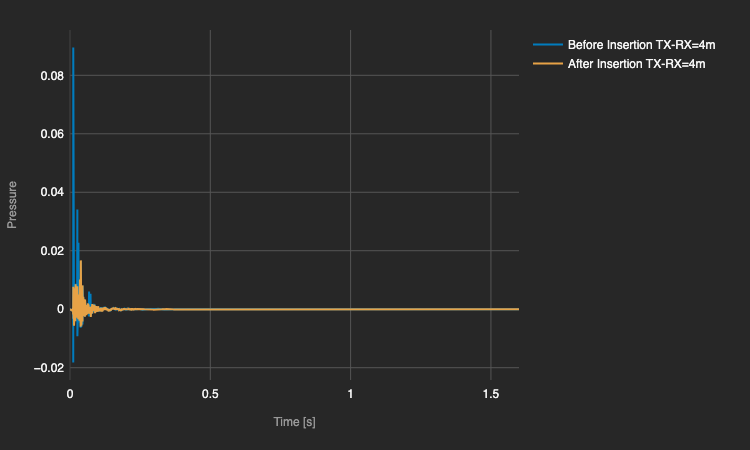
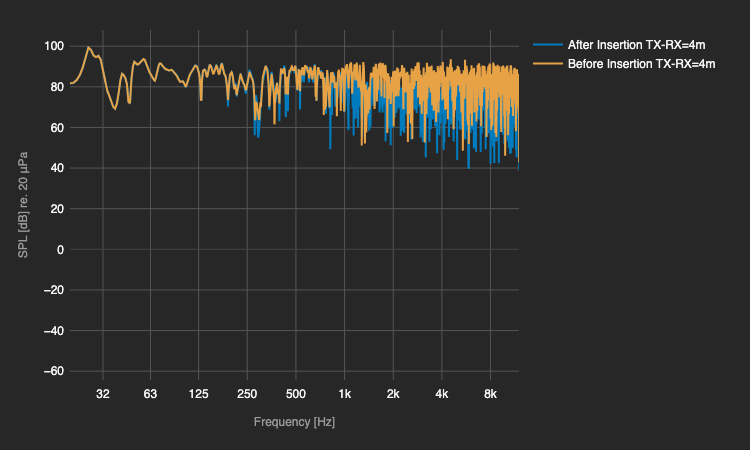
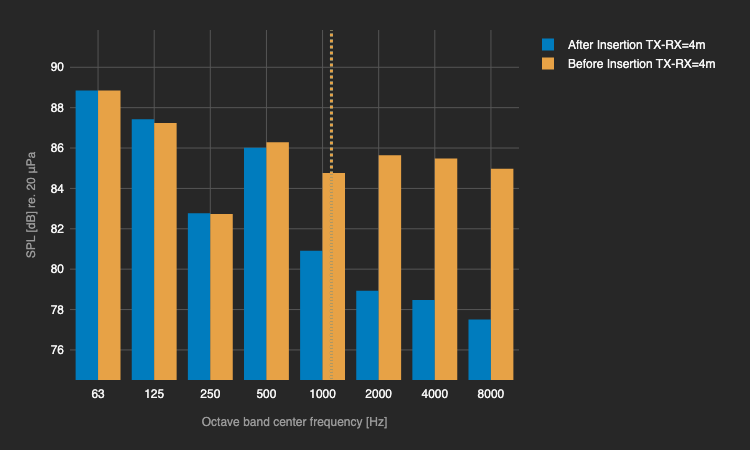
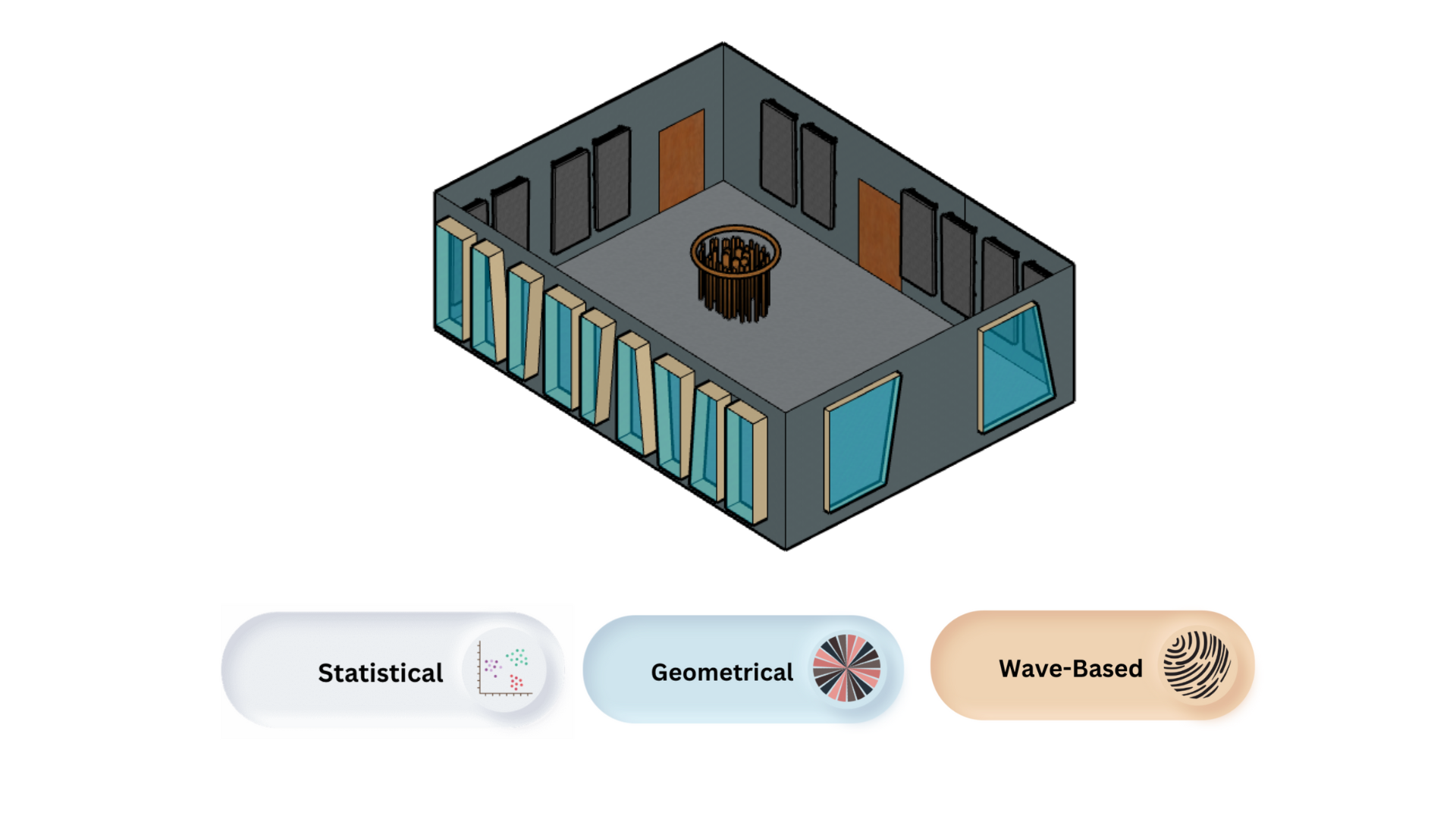
Lab measrument @TU Delft
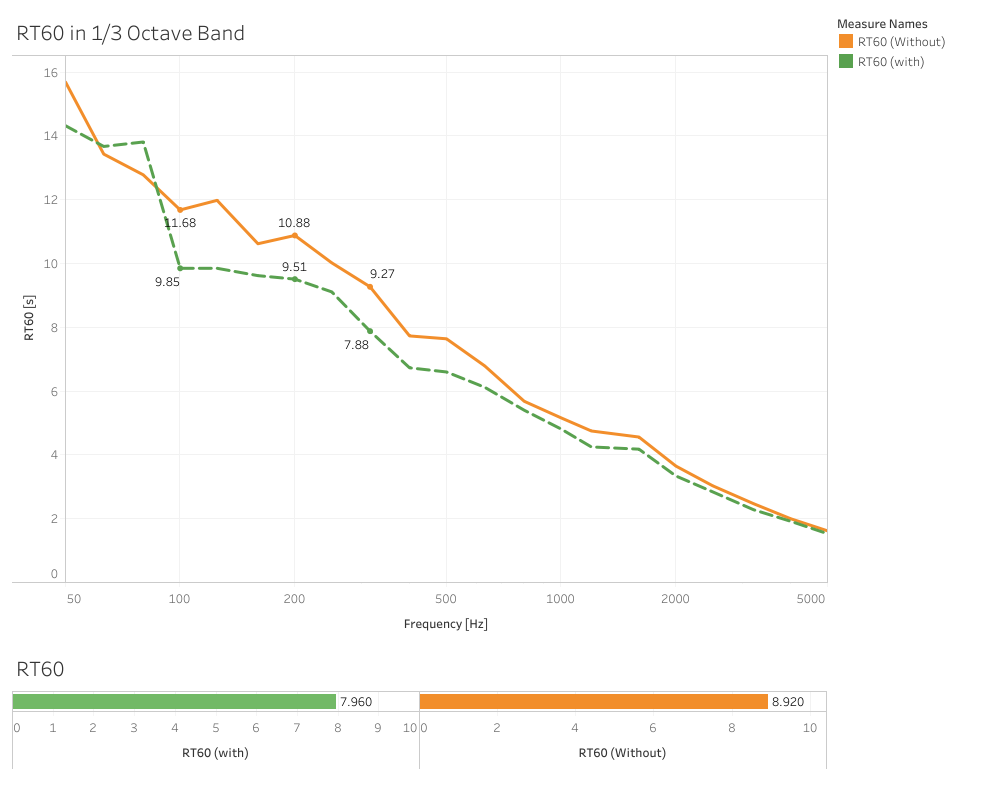
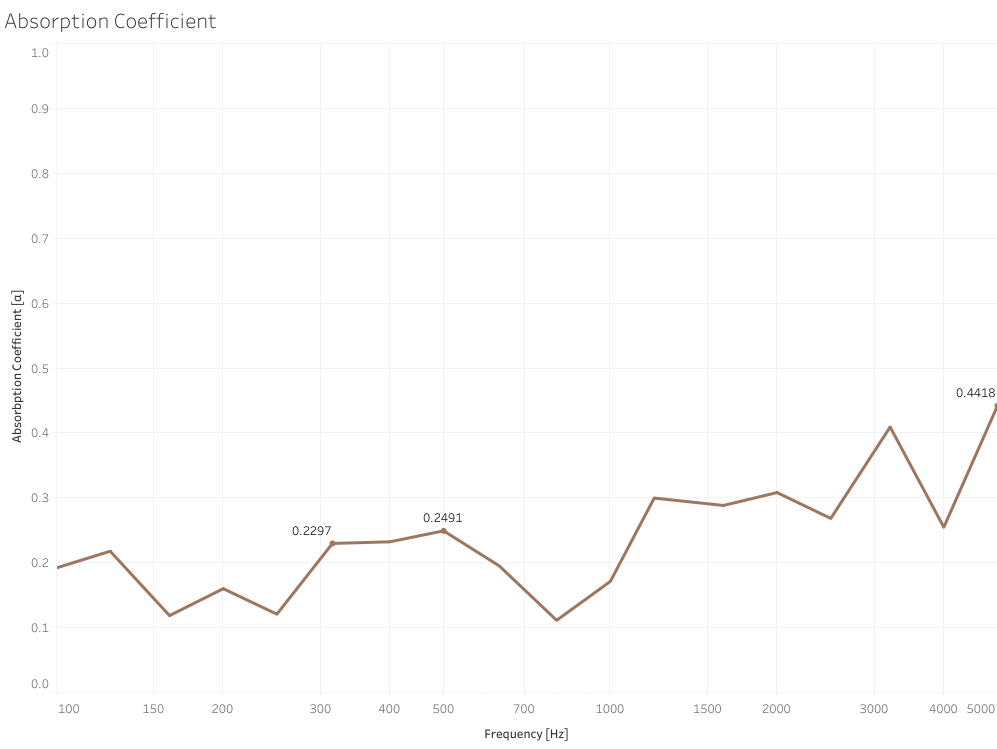
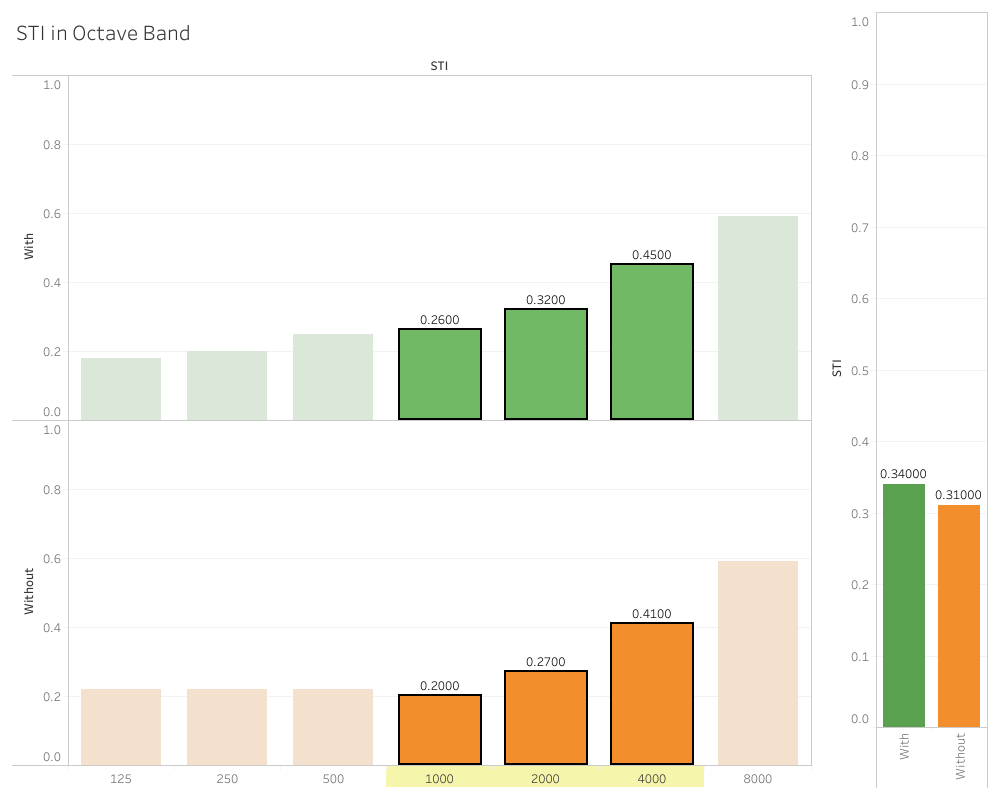
In situ measrument
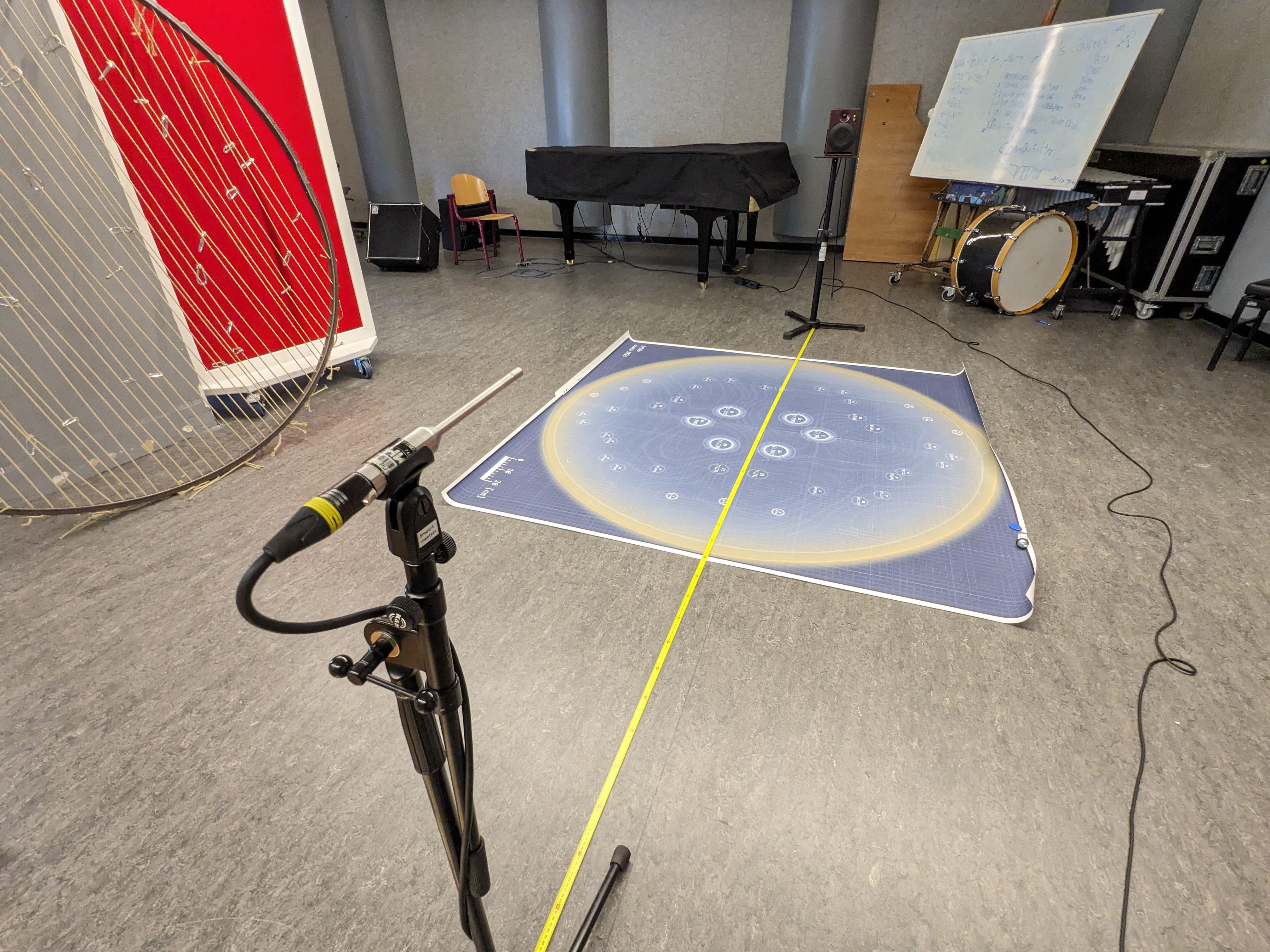
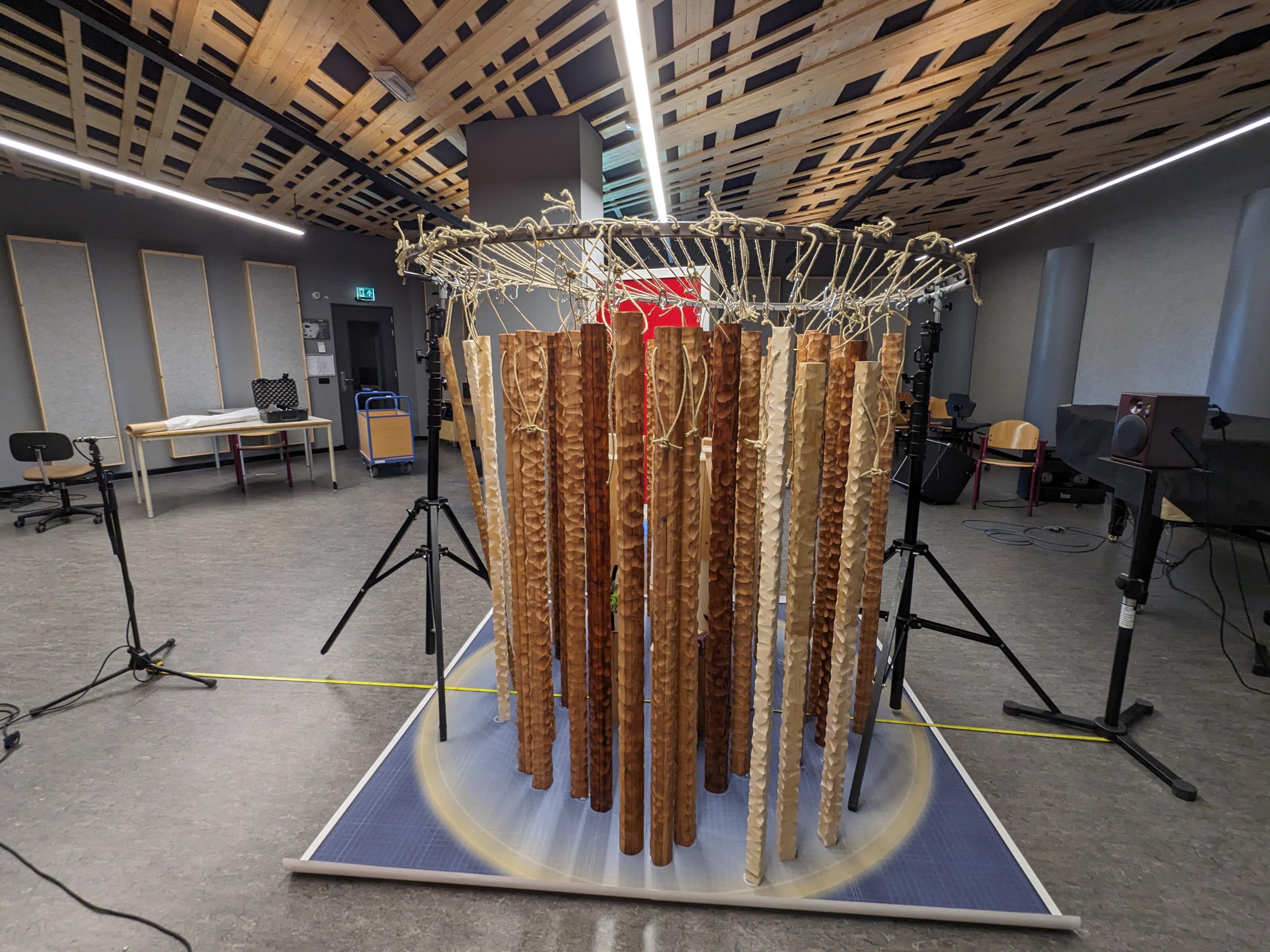



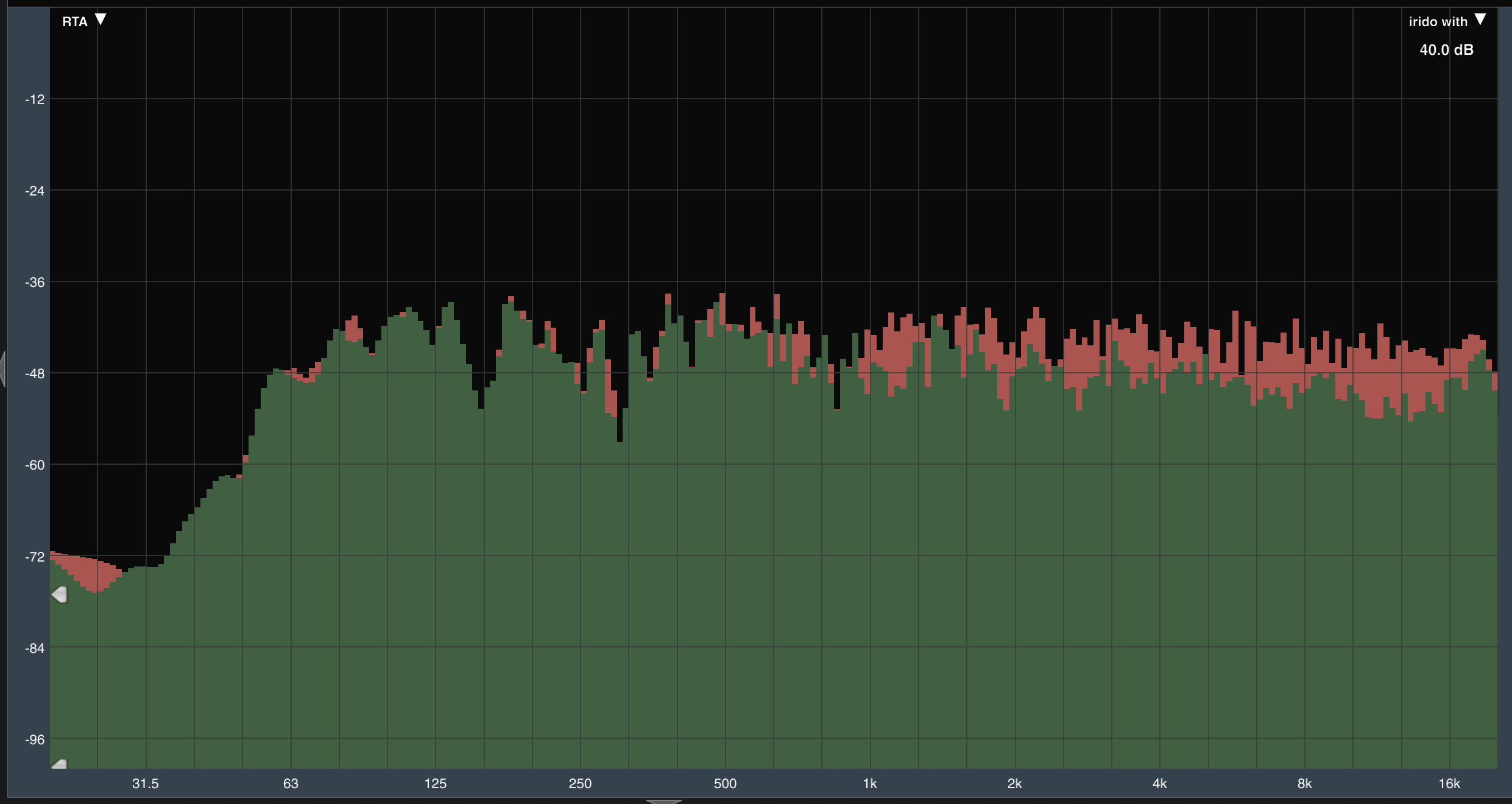
Simulation vs measrument
Measrument (Tangible Twin) Insertion Loss Frequency Response aligns with simulation in Semi-Reveratation room (Digital Twin). Meaning it's a functional Sonic Crystal.
- © Jeremy Leung
- Design: @defectedunit